In some cases it is possible to apply more rational scheme of drive directly by a cam (fig.2.i3,a), providing reduction of details number, over- all dimensions, inertial loads and more favorable force-closure. In the first construction forces are closed up at section hi of a body, which must possess enough strength for perception of drive efforts. In the second construction extent of a loaded section hi is much smaller, which reduces mass and inertia forces, acting in mechanism.
Rationality of я construction largely depends upon correct choice of power circuit design, determining perception and closure of loads, acting in a construction. Power circuit design is considered to be rational if the forces are closed at the short section by element, working preferably in tension or in compression. It is expedient to use design elements, which are already present, as introduction of new ones will lead to growth of mass.
Fig.2.14. demonstrates improvement of a drive design of a machine by means of rationalization of power-circuit diagram. Drive of a rotor-machine by means of reduction gear and cone gearing is irrational.
Radial and axial forces, appearing on gears, load shafts on a body of a machine and a reduction gear. Installation has large dimensions. Drive from a flange motor through aligned reduction gear mounted directly on a machine body is considered to be expedient (fig.2.14,b). In this case reactive forces of a drive are balanced in the shortest way in reduction gear body, without causing complementary loads on system elements. Overall dimensions of an installation are sharply reduced. Besides, all drive mechanisms become closed, which allows to organize their correct lubrication.
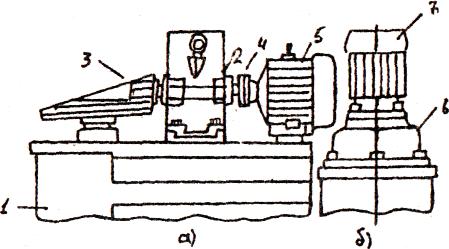
Fig 2.14. Rationalization of power-circuit
design of a machines,b, -old and new designs respectively;
1-rotor-mashine;
2- reduction-gear;
3-cone gearing;
4- clutch;
5-motor, usual;
6- aligned reduction gear;
7- flange motor
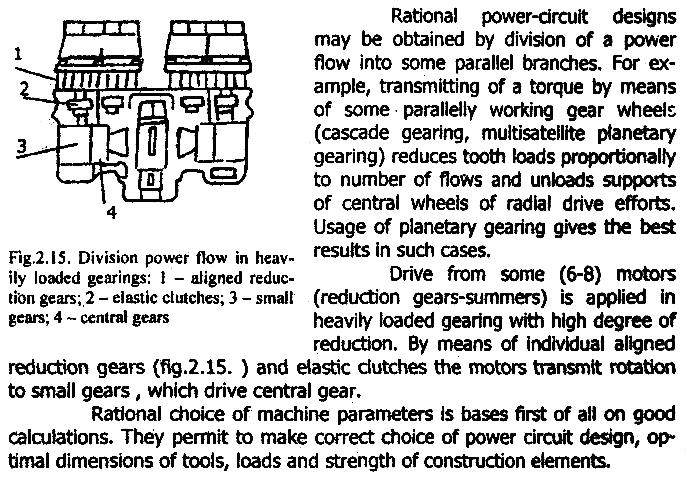
As an example, fig.2.16.shows overall dimensions of motors with the same power, the same average effective pressure and average piston rod, but with different ratios of stroke to cylinder diametre (S/D=1,4 in the fig.a, S/D=1 in the fig.b). Besides S/D reduction in fig.b we see reduction of piston night and of the length of connection rod (H=0,8 and L=l,6 instead of H=D and L=1,8D, as in fig.a). On the whole considerable profit in sizes and mass is gained.
With S/D, H and L reduction, the pressure on cylinder walls increases, that's why increase of carrying capacity of a piston by-means of improvement of lubrication and correct choice of material for piston and cylinder are considered to be necessary conditions providing application of short-stroke circuits.
Назад Оглавление Вперед



